Immunology and Systemic Inflammation Biomarkers Among Saudi Patients with Sickle Cell Anemia in Asymptomatic Steady State Condition
Authored by Fadwa M Alsharif
Abstract
Background & Objective: Sickle cell anemia
(SCA) comprises an inherited blood disorder that is lifelong and
affects many people globally. Despite progress in therapy, SCA is a
considerable cause of mortality and morbidity. This study was designed
to measure the immunological parameters and inflammatory cytokines of
Saudi patients with sickle cell anemia (SCA) in asymptomatic steady
state.
Material and Methods: Fifty asymptomatic
sickle cell anemia patients and fifty age- and sex-matched healthy
non-sickle cell disease subjects were involved in this study.
Results: The number of white blood cells,
neutrophil, lymphocytes, eosinophils, basophils, CD3, CD4 and CD8 count
were significantly elevated in stable-state SCA patients when compared
with healthy controls. In addition, the mean value of CRP, TNF-α, IL-2,
IL-4, IL-6 and IL-8 were significantly elevated in stable-state
SCApatients when compared with healthy controls.
Conclusion: High levels of serum cytokines and immune system activation are evident in Saudi SCA patients in asymptomatic steady state.
Introduction
Sickle cell anemia (SCA) is a genetic red blood cells
(RBCs) disease lead to vaso-occlusion and hemolysis due to abnormal
sickle shape and rigid RBCs [1]. Patients with SCA usually suffer from attacks of vaso-occlusive pain, poor quality of life [1,2]. About 275000 individuals suffer of SCA as new cases annually as estimated by WHO [3-5]. Sickle cell anemia (SCA) is an incurable chronic medical problem with homozygous for hemoglobin S (HbS) [6] that induce tissue ischemia and infarction due to vascular occlusion that initiates inflammatory responses [7,8].
Multiple co-morbidities usually associated with SCA as pulmonary hypertension, acute chest syndrome, strokeleg ulcers [9] and spleen infarction especially in subjects living at high altitudes [10].
Cardiac arrest, pulmonary embolism, heart failure, infections,
multi-system failure and stroke are the common causes of death among
patients with SCA [11-13].
Life-threatening infections due to insufficiency of immune system in
patients with SCA is common, especially with Streptococcus pneumoniae
and Haemophilusinfluenzae [14].Therefore,Moreover,crisis in SCA is precipitated by infection [15].
This study was designed to measure the immunologic
parameters and inflammatory cytokines of Saudi patients with sickle cell
anemia (SCA) in asymptomatic steady state.
Subjects and Methods
Subjects
Fifty sickle cell anemia Saudi patients in stable
state that presented at the Hematology Department, King Abdalaziz
University Hospital were randomly recruited into the study from the
available patients in the Hematology Department out clinic. Cases were
selected from patients whose blood samples were submitted to the
hematology section for hemoglobin electrophoresis, which was either
advised by their treating doctor or was performed to confirm a positive
sickling test. All confirmed patients of sickle cell haemoglobinopathy
diagnosed by the presence of Hemoglobin 'S' band on hemoglobin
electrophoresis and only homozygous Sickle cell disease patients
(patients whose electrophoresis showed presence of Hemoglobin 'S' band
with or without Hemoglobin 'F' band - HbSS genotype) were included in
the study. Apparently fifty healthy subjects of both gender and age
matched subjects were enrolled and considered as control group.Informed
consent was signed by all participants. Exclusion criteria included
sickle cell disease patient with concurrent HIV or overt infection.
Also, SCA patient with painful vaso-occlusive crisis (VOC) with
musculoskeletal bone.
Methods
Evaluated Parameters
Flow cytometry analysis: The human
leukocyte differentiation antigens CD3, CD4 and CD8 (Beckman Coulter,
Marseille, France) five microliters of appropriate monoclonal antibody
was added to fiftyμL of a whole blood sample and incubated for 15
minutes at troom temperature. The samples were analyzed by flow
cytometry using Cytomics FC500 and CXP software (Beckman Coulter) [16].
Analysis of peripheral blood cells: A Beckman Coulter AcT 5diff hematology analyzer was used to apply total and differential peripheral blood cells count analysis [16].
Inflammatory cytokine analysis: Serum IL-2,
IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, C-reactive protein (CRP) and tumor necrosis factor
alpha (TNF- α) levels were measured with highly sensitive ELISA kits
(Quantikine ELISA kits) via R&D Systems Inc., Minneapolis, MN [17].
Statistical analysis: Independent t-test was
used to compare differences between both groups. Statistical analysis of
data was performed using SPSS (Chicago, IL, USA) version 17. All data
were expressed as the mean ± SD. P<0.05 indicated statistical
significance.
Results
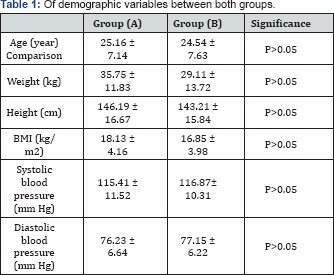
BMI: Body Mass Index .
Regarding the demographic variables, both groups were considered homogeneous (Table 1).
The mean age of the SCA group was 25.16±7.14 years, where the control
group was 24.54±7.63 years. There were no significant differences in
weight, height, body mass index (BMI), systolic blood pressure and
diastolic blood pressure between both groups.
The number of white blood cells, neutrophil,
lymphocytes, eosinophils, basophils, CD3, CD4 and CD8 count were
significantly elevated in stable-state SCA patients when compared with
control group (Table 2).
In addition, the mean value of CRP, TNF- α, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-8
were significantly elevated in stable- state SCA patients when compared
with normal controls (Table3).
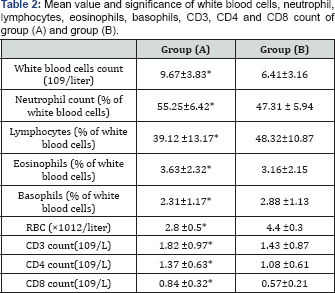
(*) indicates a significant difference between the two groups, P < 0.05.
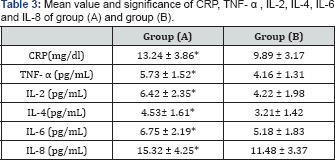
CRP: C - reactive protein ; IL-2 :Interleukin-2;
IL-4: Interleukin-4 ; IL-6:Interleukin-6 ; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor -
alpha ; IL-8 : Interleukin-8; (*) indicates a significant difference
between the two groups, P < 0.05.
Discussion
Sickle cell anemia is now the world's most common
genetic defects. About 5% of the population carry a haemoglobinopathy
trait worldwide, there are about 300,000 born annually worldwide with
hemoglobin disorder [18]. Despite the significant increase in research and number of published articles on SCA and its complications remain elusive [19]. Many authors stated that SCA is well recognized as a chronic inflammatory disease [20-22] as C-reactive protein (CRP) and other cytokines are elevated in steady state SCD compared with normal subjects [23]. In addition, researches on animals and human being with SCA proved elevation in inflammatory cytokines [24-28].
However, the results of our study confirm elevation of inflammatory
cytokines among SCA patients, our findings agreed with many previous
studies.
The possible mechanism that makes inflammatory
cytokines increased in patients with SCA which include every short
half-life and lies of sickle red cells (RBC) and increased protein
synthesis and catabolism [29,30]. However, systemic inflammation is induced with chronic hemolysis even among steady state SCA [31], In addition transient vaso-occlusive events and subclinical vascular endothelial injury [32].
Moreover, enhanced adhesiveness of sickle reticulocytes and reversibly
sickled erythrocytes to the vascular endothelium play a role in
increased level of inflammatory cytokines in patients with SCA [33,34].
Concerning immune system parameters, results ofthe
present study confirms immune system activation among SCA patients, our
findings agreed with many previous studies. Buison and colleagues &
Hyacinth and colleagues proved that patients with SCA suffer from
malnutrition that adversely affect growth and delay muscloskeletal
development [35,36].
However, insufficient performance of immune system, endothelial
activation and increased inflammatory cytokines are usually associated
with malnutrition [37-41].
While, Duitsand colleagues stated that elevated inflammatory cytokines
enhance chemotactic stimuli that result in elevated neutrophil
percentages in steady state SCA patients [42].
The present study has points of strengths and
limitations. The major strength point is the randomization nature of
this study, as subjects were selected randomly out of the available
subjects. In the other hand, the small sample size is the limitations in
the present study. Finally, the results of the present study concluded
that levels of serum cytokines and immune system activation are evident
in Saudi SCA patients in asymptomatic steady state. Moreover, more
researches are needed to measure the impact of many life style
modifications on modulation of inflammatory cytokines and immune system
activation in SCA patients.
Conclusion
Within the limits of the present study, it was
concluded that SCA increase the levels of serum cytokines and immune
system activation are evident in Saudi SCA patients in asymptomatic
steady state.
To Know More About Current Research in Diabetes & Obesity
Journal Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/crdoj/index.php
https://juniperpublishers.com/crdoj/index.php



Comments
Post a Comment