Drug-Induced Generalized Skin Eruption in a Diabetes Mellitus Patient Receiving a Metformin Plus Simvastatin in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital in Punjab
CURRENT RESEARCH IN DIABETES & OBESITY JOURNAL JUNIPER PUBLISHERS
Authored by Ashish Baldi
Abstract
Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are a main cause for morbidity and mortality. Diabetes mellitus is the most common metabolic disorder. Patients suffering from hypertension with diabetic together get several consequences. The usage of an oral antidiabetic drug is specified in patients in whom diabetes is not under controlled with diet and physical activity. Metformin is an important antidiabetic agent belongs to class biguanide. Metformin is proposed as a drug of choice for the treatment of type-2 diabetes, especially for overweight patients. An important side effect of metformin, similar to other oral antidiabetic drugs, is hypoglycemia. However, there are furthermore other rare adverse effects of this drug. Here, the author reports a rare case of allergic reactions caused by metformin in this case report.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; ADR's; Metformin; Drug allergy
Case Report
A 47-year-old man visited to the hospital complaining of an illness for which he was prescribed metformin 1000mg daily with other drug combination such as Ramipril 10mg once daily, Simvastatin 40mg at night, Aspirin 75mg once daily. The patient had been recently diagnosed for diabetes mellitus. The (RBS) random blood sugar level reported at that time was 271mg/dL. The physician had prescribed metformin 1000mg/day for type 2 diabetes. The patient developed skin reaction on his lower limbs, lower back, buttocks and fever after starting this drug. The skin reaction were round/oval erythematous macules, pain while touching and palpable purpura patches [1].
Metformin-induced vasculitis was suspected and the patient was advised to stop metformin. A detailed history revealed that the patient was on Ramipril 10mg once daily and Simvastatin 40mg at night already for treatment of hypertension and hyperlipidemia.The patients were kept under observation which shows that after one week, the skin rash were improved, and disappeared after 10 days later. The patient refused for skin biopsy or other diagnostic tests even the facility for the skin biopsy weren't available in the hospital. In the absence of these, this case was diagnosed as a case of vasculitis probably due to metformin. Oral prednisone 60mg daily and cream of synthetic glucocorticoid named as fluticasone was initiated, with improvement at first, but the lesions reappeared when the treatment was stopped. Other drug simvastatin was all discontinued, and again the lesions reappeared after the corticosteroid dose was reduced. Rosiglitazone belong to the thiazolidinedione's class of oral diabetes medication was initiated as a replacement for metformin, the lesions did not return, and the other medications were restarted without relapse. A Naranjo score of 6 was calculated, indicating a probable association between metformin use and fixed drug eruption Table 1.
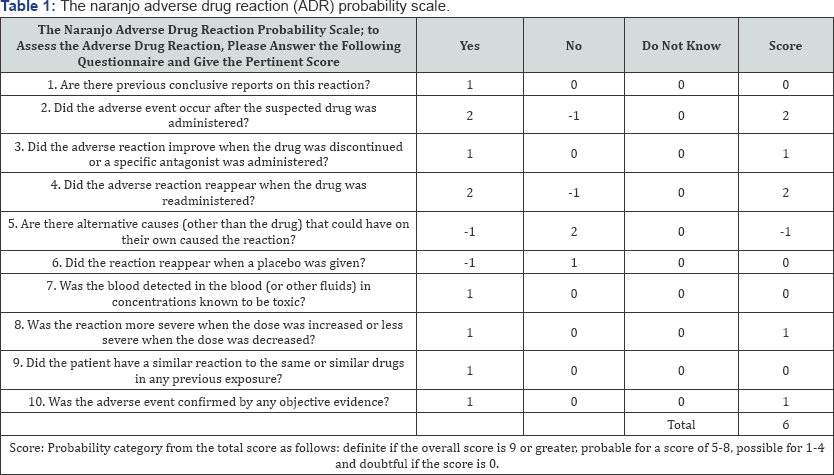
The Naranjo scale was used to categorise the probability that an adverse drug reaction or adverse event is related to drug treatment based upon a list of weighted questions. The ADR is assigned to a The Naranjo criteria do not take into interpretation drug-drug interactions. Drugs are evaluated independently for causality, and points deducted if another factor may have resulted in the adverse event, thereby weakening the causal association [2].
Discussion
Metformin is the first-line of medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Particularly in people who are overweight. Metformin is usually well tolerated [3]. The most common side effects of the metformin include diarrhea, nausea and abdominal pain, gastrointestinal irritation, increased flatulence, skin reaction like palpable purpura patches and metformin is more commonly associated with gastrointestinal side effects than most other antidiabetic drugs [4]. The metformin has a low risk of causing low blood sugar [5]. High blood lactic acid level is a concern if the drug is prescribed inappropriately and in overly large dose [6]. For palpable purpura patches the clinical consequence of this is still unknown or might be due to allergic reaction to metformin. Several reports suggest that serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare; however, this product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems [1]. High fever, diarrhea, vomiting, diuretics or excess sweating may cause dehydration and increase the risk of lactic acidosis. Older adults may be at greater risk for side effects such as low blood sugar or lactic acidosis [7,8].
Conclusion
In the present case, the initial generalized skin eruption may have been induced by an allergic reaction to metformin which is very rare. Close attention should be paid to patients receiving this drug with a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia and the patient were on drug simvastatin.
To More articles in Current Research in Diabetes & Obesity
Journal Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/crdoj/index.php
For more about Juniper Publishers please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/video-articles.php


Comments
Post a Comment